Security Camera Installation Best Practices
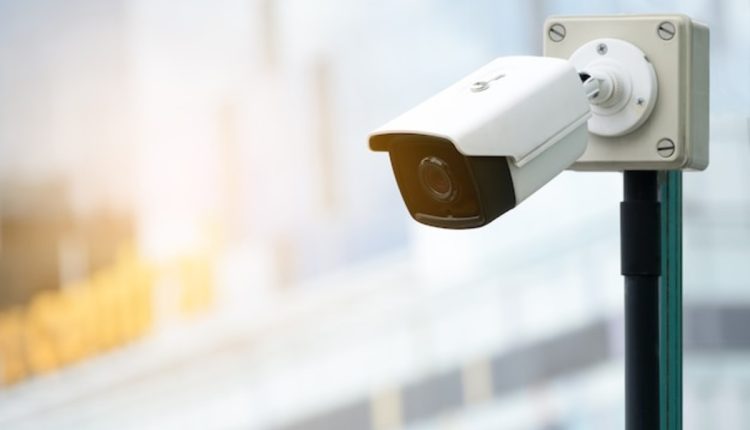
Security cameras can help residents feel more at ease in their home environment, but they must be correctly installed to monitor any trouble spots or potential risks in their house. The Interesting Info about 4g solar camera.
That means ensuring they are situated to monitor entry points and living areas and can capture footage without drilling holes into walls or fishing cables through insulation. In addition, ladder safety rules must also be observed.
Plan Your Positions
Home security camera systems provide peace of mind to you and your family, offering adequate protection from intruders while giving you extra peace of mind. When planning the camera placement for optimal coverage on your property, we will consider important factors like optimizing camera angles, critical areas, weatherproofing measures, and privacy issues to ensure a successful installation experience.
Before beginning installation, draw an outline or sketch of your home and property to mark out potential locations for cameras and sensors. This allows you to experiment with various configurations until you find your ideal layout before drilling holes in walls. Apps offering live camera view help plan as well.
Your outdoor cameras should ideally cover entry and exit points of your property as well as gates or garages, while indoor cameras should be located in high-traffic areas like hallways and living rooms to increase the likelihood that criminals will be caught on film and brought to justice. Avoid placing indoor cameras in bedrooms, as this would likely be seen as an invasion of privacy.
As well as placing cameras strategically, you should pay special attention to ambient lighting. This will determine the quality of the footage as well as your ability to see movement and faces clearly in footage captured from multiple cameras. When possible, install exterior lighting fixtures for improved ambient lighting.
Another mistake many homeowners make is that they need to pay more attention to the importance of protecting their home network. Implementing strong encryption on your router and setting a secure WiFi password are essential measures that will minimize unauthorized access. Also, consider isolating security camera networks from main networks to secure them against hackers further.
Be sure to stay current with your camera firmware and software updates; these fixes aim to address bugs or vulnerabilities and will strengthen your system against hacking attempts.
Choose a Power Source
Wired security cameras require power for operation. This source may be hardwired into your home or business and connected to either your DVR, internet feed, router, analog camera setup, etc. Some models even utilize Power over Ethernet (PoE), eliminating the need for two separate cords for video and power sources.
Your power source selection is vital in order to maintain a stable connection for your security camera. Wireless connections tend to drop signal, making wired connections much more reliable and preventing data theft since data travels via private networks instead of public WiFi.
Based on your needs, a power distribution box or power adapters may be more appropriate. A distribution box allows for easier management and installation by consolidating power supplies for multiple cameras into a central location, while for buildings of 4 or fewer security cameras, a power adapter should suffice.
Before purchasing a power supply, you must calculate how many cameras and their total wattage you plan to use simultaneously. This will enable you to determine its maximum capacity while avoiding oversizing it.
An analog or HD-SDI camera requires both coax wires for video transmission and power wires to operate correctly. You could run separate cables for each of these requirements; however, most CCTV professionals opt for “Siamese Cable,” a manufactured coax cable with built-in power wires allowing easy connection of coax and separate power wires without cutting or soldering separately.
Wired security cameras tend to be more reliable than wireless ones due to being less vulnerable to interference or dropped signals. When installing them in attics or soffits, cables can often be run through these spaces for easy and discreet installation.
Run the Cables
Correctly wired security camera systems will offer seamless data and power transmission, improving functionality and aesthetics. Planning, cable types knowledge, and best practice guidelines are essential to creating a successful project; by following them, you’ll avoid common installation errors that lead to data loss and poor video quality.
Before beginning to wire cameras, you must consider their locations and proximity to a central recording station. This will enable you to determine how far apart they should be and whether any additional equipment, such as signal boosters, is necessary. Furthermore, please take note of any power requirements for each camera as well as an electrical outlet nearby where you can connect them.
Once you’ve decided upon camera locations and an optimal cable routing strategy, drilling holes to install cables is the next step. To minimize disruption to existing wiring systems and ensure optimal results for wired security cameras, drilling should occur from within your house rather than outside it.
As you run cables through your home or business, they must stay clear of heat sources and high-voltage lines to reduce the risk of wire damage and improve video quality. A junction box should also be installed outside for convenient connectivity of cameras to power and network cables.
As it’s also essential that cables be protected from both human and animal tampering, it is also crucial that you consider where you will store your cables. Running them under an overhang or porch roof overhang can prevent squirrels or birds from accessing them; alternatively, burying PVC or metal conduits might provide added security.
Note that sunlight exposure will have an enormous impact on the performance of your camera system over time, significantly since UV rays from direct sunlight can degrade cable over time and hasten its premature failure. Therefore, placing them in conduit or protected locations such as under a soffit will ensure optimal performance and ensure their longevity.
Mount the Cameras
Once your power source and cables are in place, it’s time to mount your cameras. Be mindful of any potential complications; for instance, indoor installation requires that cameras are within approximately 5.5 feet (1.8 meters) from an outlet so they continue working if power goes out.
If your camera needs to be mounted at an elevated location, make sure it can be reached easily without climbing on anything hazardous or using tools. Also, consider choosing an installation spot with favorable temperatures and conditions in which to install them.
Many security camera kits include mounting templates that make this step straightforward. Use this template to mark where each camera should go before drilling holes for it using a drill bit that matches up with its respective screws in your kit – or else cracking or damaging drywall may occur!
Wired cameras require connecting their cable to an electrical source; if this task seems daunting to you, hire an electrician instead. When using wireless systems instead, the camera itself has its backup battery to keep operating during any power outages.
Once your cameras are mounted, the setup should go smoothly. If any questions arise during the design of your security cameras, feel free to consult your security solution provider; they are there to provide advice that will ensure the maximum effectiveness of your home security camera system.
Read also: Small Spy Camera – What to Look For in a Spy Camera